Impact on systems
Many startups aspire to change the entire system they are operating in, including healthcare, financial, political and education systems. Examples could include more equitable access to healthcare, or changing the way financial resources move around a system. Any time a startup is trying to tilt a system to a more impactful equilibrium, this is an example of an indirect pathway to creating impact.
VCs might also be operating at the systems level, making multiple investments targeting a system, in the hope that they can create a new, system-wide, status quo. Ascension Ventures is a good example of this, with a Fair By Design fund aiming to tackle systemic challenges leading to the poverty premium, and a Good Food Fund that aspires for the same in terms of healthy eating.
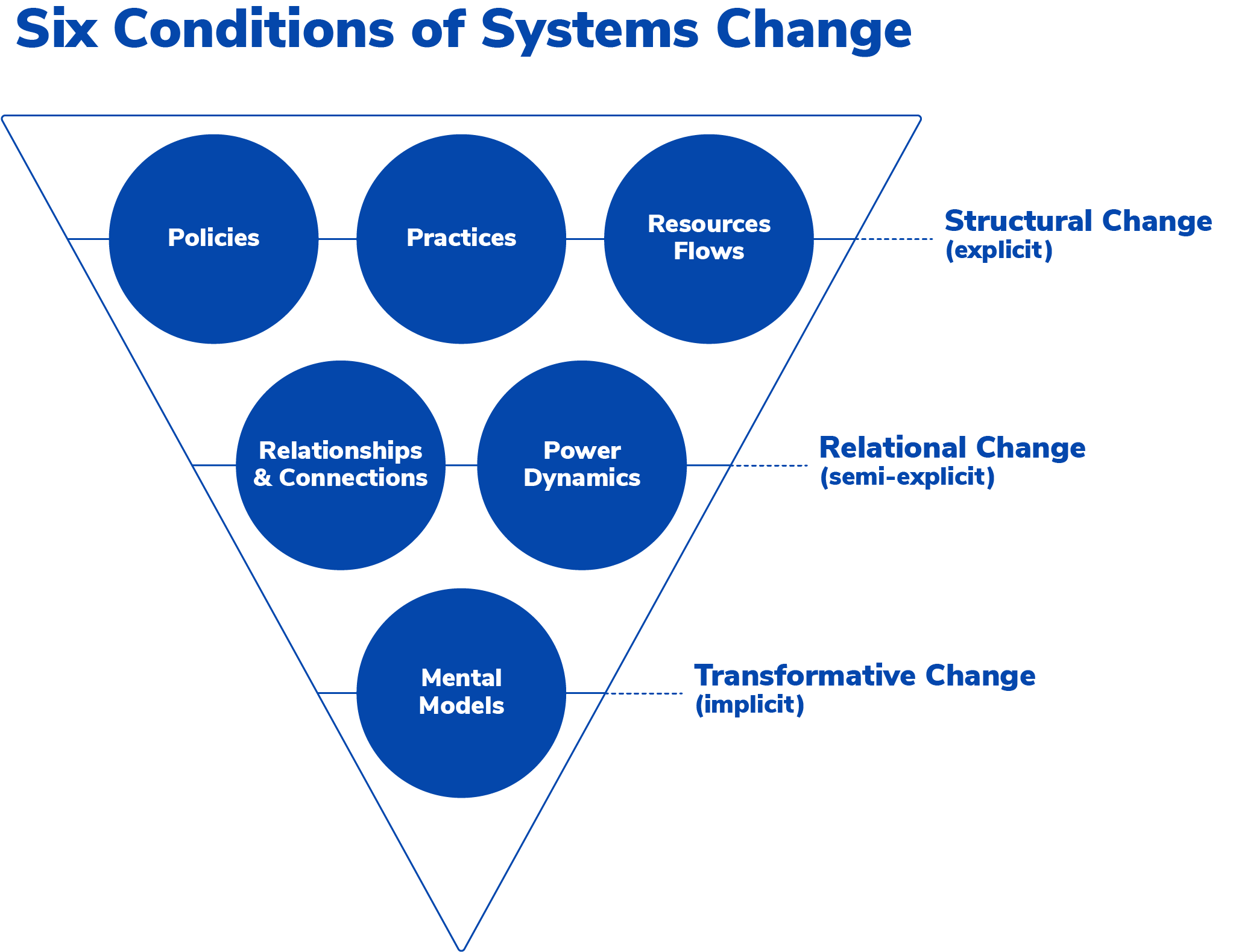
A helpful framework to think about systems change, is FSG's inverted triangle framework. This highlights six systems conditions that determine the outcomes that the system generates. These conditions are often the targets of systems change interventions.
Here are some examples of startups trying to tilt systems against these systems conditions:
| System Condition | Startup | Approach |
|---|---|---|
Policies | Its platform gives workers the tools to organise and take collective action to change policies for working conditions | |
Practices | Recruitment software that de-biases the recruitment and selection process, leading to a fairer way of hiring | |
Resource Flows | Making it easier for capital to flow to impactful business models | |
Relationships & Connections | Making it easier for organisations to engage with their communities | |
Power Dynamics | By enabling remote working through its distributed HR platform, Oyster is trying to shift the balance of power to those who are underserved by the current labour market | |
Mental Models | Changing mental models often happens organically when startups demonstrate a radically better way of doing things. Paired is a good example of trying to shift relationship care away from crisis resolution, towards proactive management of relationship health, as a way of improving mental and physical health. |
For any organisation trying to create systems change, it's worth going through a process to analyse the system in question and identify where the key levers for change are. Here is an example of the process that Oyster went through to map out and understand how it wanted to change the employment system to a more equitable status quo.
The process included:
Mapping the system:
What problem have we observed?
What are the systems change conditions that drive it?
What would a better version of this system look like?
How might we close the gap?
Focusing on impact on people:
What outcomes for people do we want the new system to generate?
What are the key levers to achieving this?
What might go wrong along the way?
Last updated